## Suggested URL Slug
french-pension-protests
## SEO Title
French Pension Protests: Why Macron’s Reforms Sparked Outrage
## Full Article Body
France, a nation celebrated for its rich history of social movements and a deep-seated commitment to workers’ rights, finds itself once again at a critical juncture. The recent pension reforms, pushed through by President Emmanuel Macron’s government, have ignited a firestorm of public discontent. Amidst a backdrop of political and economic turbulence, few issues have illuminated the fault lines of French governance quite like these highly unpopular pension changes. This article delves into the heart of the French pension protests, exploring the reasons behind the widespread opposition, the implications for French society, and what the future may hold.
The controversy surrounding the pension reform is not merely a policy debate; it’s a clash of ideologies and a testament to the enduring power of collective action in France. The government’s decision to raise the retirement age from 62 to 64, without a parliamentary vote, has been perceived by many as an affront to democratic principles and a betrayal of social solidarity.
### Understanding the Pension Reform: What’s at Stake?
At its core, the French pension system is a complex web of rules and contributions designed to provide financial security for citizens in their retirement. For decades, the standard retirement age has been a cornerstone of this system, reflecting a delicate balance between public finances and individual well-being.
The Macron administration’s rationale for the reform centered on the need to ensure the long-term financial viability of the pension system. Proponents argued that an aging population and declining birth rates would inevitably lead to a deficit, necessitating an increase in the retirement age to maintain pay-as-you-go funding.
However, the proposed changes have met with fierce resistance from a broad spectrum of French society. The core of the opposition lies in several key areas:
* **The Retirement Age Increase:** The most contentious aspect is the mandated rise in the retirement age to 64. Critics argue that this disproportionately affects manual laborers and those in physically demanding jobs, who may not be able to sustain such work for an additional two years.
* **The Method of Passage:** The government’s decision to bypass a full parliamentary vote and utilize Article 49.3 of the French Constitution – a mechanism that allows the government to pass legislation without a vote unless a motion of no confidence is passed – has been widely condemned as undemocratic and a sign of executive overreach.
* **Social Inequality:** Opponents contend that the reform exacerbates social inequalities, placing a greater burden on working-class individuals while potentially benefiting higher earners who can afford to retire later or invest in private pensions.
### The Fury Unleashed: Protests and Public Reaction
The announcement and subsequent implementation of the pension reform have been met with immediate and sustained public outcry. From the bustling streets of Paris to the historic squares of Marseille, demonstrations have erupted, drawing millions of participants from all walks of life.
The protests have been characterized by their sheer scale and diversity. Unions, student groups, and ordinary citizens have united under a common banner of opposition, demanding the withdrawal of the reform. The visual spectacle of these marches, often accompanied by vibrant banners, passionate chants, and a palpable sense of collective grievance, has garnered international attention.
Key elements of the protest movement include:
* **Mass Demonstrations:** Organized by major trade unions, these marches have seen hundreds of thousands, and at times millions, take to the streets nationwide.
* **Strikes:** Various sectors, including public transport, energy, and education, have experienced widespread strikes, disrupting daily life and highlighting the economic impact of the discontent.
* **Civil Disobedience:** While largely peaceful, some protests have seen instances of clashes with police and acts of vandalism, reflecting the depth of frustration and anger.
* **Solidarity and Unity:** The broad coalition of groups participating in the protests underscores a shared concern for social justice and a desire to protect France’s welfare state.
The government’s response has been a mixture of steadfastness and attempts at dialogue. While President Macron has largely defended the necessity of the reform, acknowledging the public’s anger, his administration has also engaged in discussions with union leaders, though these have often yielded little in terms of substantive concessions.
### Deeper Implications: What This Means for France
The French pension protests are more than just a reaction to a specific policy; they represent a deeper societal conversation about the future of work, social welfare, and the very nature of the French republic. The ramifications extend beyond the immediate policy outcome.
* **Erosion of Trust in Government:** The perception that the government has disregarded public opinion and democratic processes can lead to a significant erosion of trust between citizens and their elected officials. This can have long-term consequences for political stability and civic engagement.
* **Strengthening of Social Movements:** The success of unions and protest groups in mobilizing large segments of the population could embolden future social movements, creating a more dynamic and potentially challenging political landscape for any government.
* **Economic Impact:** While intended to bolster the economy, the widespread strikes and protests have had a tangible negative impact on various sectors, including tourism and retail. This economic disruption, coupled with the underlying fiscal challenges, creates a complex economic balancing act.
* **The Future of the Welfare State:** The debate over pensions is intrinsically linked to the broader question of how France will fund its generous welfare state in the face of demographic shifts and global economic pressures. This reform, and the reaction to it, will likely shape future discussions on social security, healthcare, and public services.
### Global Parallels and French Exceptionalism
While France’s history of robust social protest is well-documented, the current pension reform has resonated with similar debates occurring across the globe. Many developed nations are grappling with the financial sustainability of their retirement systems due to increasing life expectancies and aging populations.
However, France’s approach to these challenges often stands apart. The strong emphasis on social dialogue, collective bargaining, and the right to protest are deeply ingrained in the national psyche. This “French exceptionalism” in social and labor relations means that policy changes, particularly those affecting fundamental social rights, are met with a level of resistance that might not be seen elsewhere.
As noted by the International Labour Organization (ILO), “Social dialogue is crucial for managing the economic and social consequences of demographic change and ensuring the sustainability of social security systems.” France’s current situation underscores the vital role of this dialogue, and the potential consequences when it is perceived to be lacking.
### Looking Ahead: What’s Next for French Pensions?
The immediate future of the pension reform remains uncertain. While the law has been enacted, the persistent public opposition and the ongoing debate suggest that the story is far from over.
Several potential scenarios could unfold:
1. **Continued Protests and Political Pressure:** The widespread discontent could continue to fuel protests and strikes, creating ongoing political pressure on the government to reconsider or amend the reforms.
2. **Legal Challenges:** There is a possibility of legal challenges to the reform, based on constitutional grounds or alleged procedural irregularities.
3. **Future Revisions:** Future governments, or even the current administration under different circumstances, might be compelled to revisit and adjust the pension system to address lingering concerns and ensure long-term stability.
4. **Social Unrest:** In a more extreme scenario, prolonged and unaddressed grievances could potentially lead to broader social unrest, impacting political stability.
Ultimately, the French pension protests serve as a powerful reminder of the enduring importance of social contracts and the will of the people in shaping national policy. The debate over retirement age, worker rights, and the sustainability of social welfare systems is a complex one, with no easy answers. France’s experience offers valuable insights into the delicate balance required to navigate these challenges while upholding democratic values and social solidarity.
***
**Disclaimer:** This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal or financial advice. The views expressed herein are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of any organization.
**Sources:**
* International Labour Organization (ILO): [https://www.ilo.org/](https://www.ilo.org/)
* The French National Assembly (for constitutional information): [https://www.assemblee-nationale.fr/](https://www.assemblee-nationale.fr/)
***
copyright 2025 thebossmind.com
##
Featured image provided by Pexels — photo by Ayoub Galuia


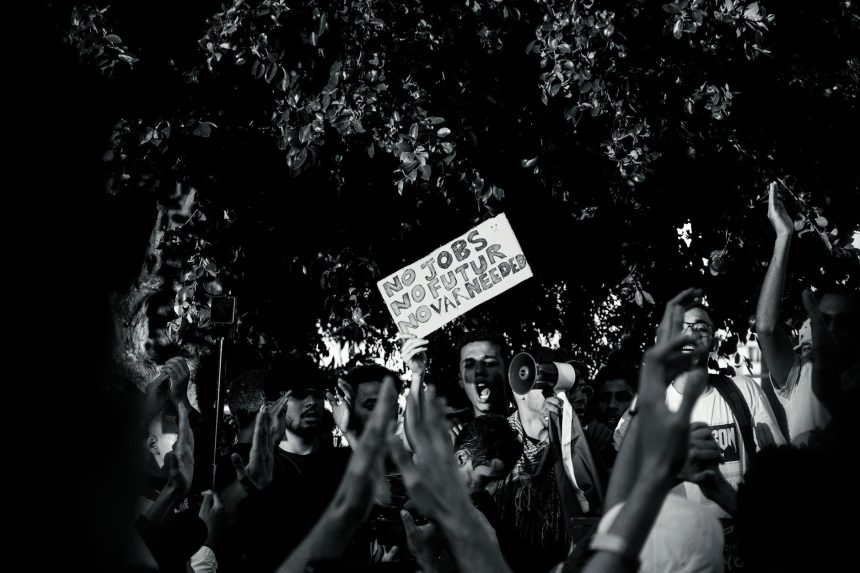
 * [https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-65000312](https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-65000312)](https://thebossmind.com/wp-content/uploads/1/2025/10/pexels-photo-34261564-1-150x150.jpeg)

![Nuclear Reactor Submarine Systems: Powering the Deep ## Nuclear Reactor Submarine Systems: Powering the Deep The silent giants of the ocean, ballistic missile submarines, represent the pinnacle of naval engineering and strategic deterrence. At their heart lies a complex and incredibly powerful system: the nuclear reactor. These underwater behemoths rely on these sophisticated powerhouses not just for propulsion, but for the sustained operation of all their critical systems, from life support to weapons deployment. A recent announcement highlighting advancements in **nuclear reactor** plant **systems** for these submarines, involving MCG Companies and its subsidiaries like JTS, Point Eight Power, and DVM Power + Control, signals a significant step forward in naval technology. This development raises fascinating questions about the future of underwater power, the intricate engineering involved, and the implications for national security. ### The Unseen Engine: Understanding Submarine Nuclear Reactors For the uninitiated, the concept of a nuclear reactor powering a submarine might seem like science fiction. However, it's a reality that has defined naval power projection for decades. Unlike conventional submarines that require frequent surfacing to recharge batteries or refuel, nuclear-powered vessels can remain submerged for months at a time. This remarkable endurance is thanks to the continuous and abundant energy generated by their onboard nuclear reactors. **How Do They Work?** At its core, a submarine's nuclear reactor functions similarly to those found in power plants, albeit on a much smaller and more robust scale. The process involves nuclear fission, where atoms of a heavy element, typically uranium, are split, releasing a tremendous amount of energy in the form of heat. This heat is then used to boil water, creating high-pressure steam. The steam, in turn, drives turbines connected to generators, producing electricity. This electricity powers everything on the submarine, including: * **Propulsion:** Turning the propeller shafts that move the submarine through the water. * **Life Support:** Generating oxygen, scrubbing carbon dioxide, and maintaining a habitable environment for the crew. * **Sensors and Sonar:** Powering the sophisticated equipment used for navigation and detection. * **Weapon Systems:** Ensuring the readiness and operational capability of ballistic missiles and other armaments. * **Internal Systems:** Running lights, communications, and all other onboard machinery. The key advantage of nuclear power for submarines is its immense energy density. A small amount of nuclear fuel can power a submarine for its entire operational life, eliminating the need for frequent refueling and allowing for extended submerged patrols. ### The Latest Advancements: A Glimpse into the Future The press release regarding MCG Companies' involvement in enhancing **nuclear reactor** plant **systems** for ballistic missile submarines points to a continuous drive for innovation in this critical sector. While specific details of the advancements are often classified, we can infer the general directions of progress. **Key Areas of Focus for Modernization:** * **Increased Efficiency and Power Output:** Newer reactor designs are likely to be more efficient, generating more power from less fuel, and potentially allowing for faster transit speeds or greater operational flexibility. * **Enhanced Safety Features:** Safety is paramount in any nuclear application, and submarine reactors are no exception. Continuous improvements focus on passive safety systems that rely on natural physical laws to prevent accidents, even in extreme circumstances. * **Reduced Size and Weight:** Miniaturization of components and systems can lead to smaller, more streamlined submarines, or allow for more space for other critical equipment and crew amenities. * **Improved Maintainability and Reliability:** Making systems easier to maintain and more reliable reduces downtime and ensures the submarine can perform its missions without interruption. * **Stealth and Signature Reduction:** Modern naval warfare emphasizes stealth. Advancements in reactor technology may also focus on reducing the acoustic and thermal signatures of the submarine, making it even harder to detect. The involvement of companies like JTS, Point Eight Power, and DVM Power + Control suggests a comprehensive approach. JTS might be involved in the core reactor design and fuel handling, Point Eight Power could be contributing to the power generation and distribution systems, and DVM Power + Control might be focusing on the intricate control and automation aspects of the **nuclear reactor** plant **systems**. ### The Strategic Significance of Nuclear Submarine Power The ability to operate undetected for extended periods underwater is a cornerstone of modern strategic deterrence. Ballistic missile submarines, often referred to as "boomers," carry nuclear-armed missiles, providing a second-strike capability that is crucial for maintaining global stability. **Why is this so important?** 1. **Deterrence:** The survivability of nuclear submarines makes them a credible deterrent. An adversary knows that even after a first strike, these submarines can retaliate, making a pre-emptive nuclear attack an unacceptable risk. 2. **Stealth and Survivability:** Their ability to remain hidden beneath the waves ensures their survival, making them the most survivable leg of the nuclear triad. 3. **Global Reach:** Nuclear submarines can operate anywhere in the world's oceans, projecting power and providing intelligence gathering capabilities far from home shores. 4. **Continuous Presence:** Unlike aircraft or land-based missiles, submarines offer a persistent and unseen presence, providing a constant, albeit silent, message of capability. The ongoing development and modernization of **nuclear reactor** plant **systems** are therefore not just about technological advancement; they are about maintaining and enhancing a nation's strategic posture and ensuring its security in a complex geopolitical landscape. ### The Engineering Marvel: A Look Beneath the Surface Designing and operating a nuclear reactor aboard a submarine is an undertaking of immense complexity and requires an unparalleled level of engineering expertise. The environment in which these reactors operate is extreme – high pressure, limited space, and the constant need for absolute reliability. **Key Engineering Challenges:** * **Space Constraints:** Submarines are inherently confined spaces. Reactor components must be designed to be as compact and lightweight as possible without compromising safety or performance. * **Heat Dissipation:** Nuclear reactors generate significant heat. Efficiently dissipating this heat into the surrounding ocean water, while maintaining operational temperatures, is a critical design challenge. * **Vibration and Shock:** Submarines are subjected to constant vibrations from their own machinery and potential shockwaves from nearby underwater explosions. Reactor systems must be robust enough to withstand these forces. * **Radiation Shielding:** Protecting the crew and sensitive electronic equipment from harmful radiation is paramount. Extensive shielding is integrated into the reactor design. * **Crew Training and Expertise:** Operating and maintaining a nuclear reactor requires highly trained and dedicated personnel. Rigorous training programs are essential for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of these systems. The companies involved in the recent announcement are likely contributing specialized expertise to tackle these multifaceted challenges. For instance, a company specializing in power control systems would need to develop highly redundant and fail-safe mechanisms to manage the reactor's output, even under the most demanding operational conditions. ### Beyond Propulsion: The Holistic Role of Reactor Systems It's crucial to understand that the **nuclear reactor** plant **systems** aboard a submarine are not solely for propulsion. They form the lifeblood of the entire vessel, enabling its sustained operation in an environment where external power sources are non-existent. **The Interconnectedness of Systems:** Imagine a submarine at periscope depth, conducting surveillance. The reactor is not only powering the propulsion to maintain its position but also: * **Powering the sonar arrays** to listen for distant vessels. * **Operating the periscopes and optical sensors** for visual observation. * **Maintaining the atmospheric controls** to keep the air breathable for the crew. * **Running the communication systems** to relay intelligence back to command. * **Ensuring the readiness of the missile launch systems**, should the need arise. This demonstrates the intricate interdependence of all systems, all drawing power from the central nuclear reactor. Any disruption or inefficiency in the reactor system can have cascading effects throughout the submarine's capabilities. Therefore, advancements in this area are not just about raw power but about the reliability, efficiency, and integrated functionality of the entire platform. ### The Future of Submarine Power The continued investment in and development of **nuclear reactor** plant **systems** for submarines underscore their enduring strategic importance. As naval technology evolves, we can anticipate further innovations: * **Advanced Reactor Designs:** Exploration of smaller, more modular, and potentially even more efficient reactor types. * **AI and Automation:** Increased integration of artificial intelligence and advanced automation for monitoring, control, and predictive maintenance of reactor systems. * **Longer Deployment Cycles:** Continued efforts to extend the time between refueling, allowing for even longer submerged patrols and reduced operational costs. * **Enhanced Survivability Features:** Integrating new technologies to further improve the stealth and resilience of these platforms. The press release from MCG Companies offers a tangible sign that this evolution is already underway. It highlights the ongoing commitment to maintaining a technological edge in a domain where silent, enduring power is paramount. The silent, deep-running world of ballistic missile submarines is powered by a marvel of engineering: the nuclear reactor. As nations continue to invest in these critical assets, advancements in **nuclear reactor** plant **systems**, like those being pursued by MCG Companies, will be crucial for maintaining strategic advantage and ensuring global security. The intricate interplay of physics, engineering, and operational requirements makes these underwater powerhouses a testament to human ingenuity and a vital component of modern defense. copyright 2025 thebossmind.com Source: [Link to a reputable source discussing naval nuclear propulsion or submarine technology - e.g., a government defense agency website or a well-known defense industry publication.] Source: [Link to another reputable source, perhaps focusing on the specific companies mentioned or general advancements in nuclear engineering.]](https://thebossmind.com/wp-content/uploads/1/2025/10/pexels-photo-19870007-330x220.jpeg)



